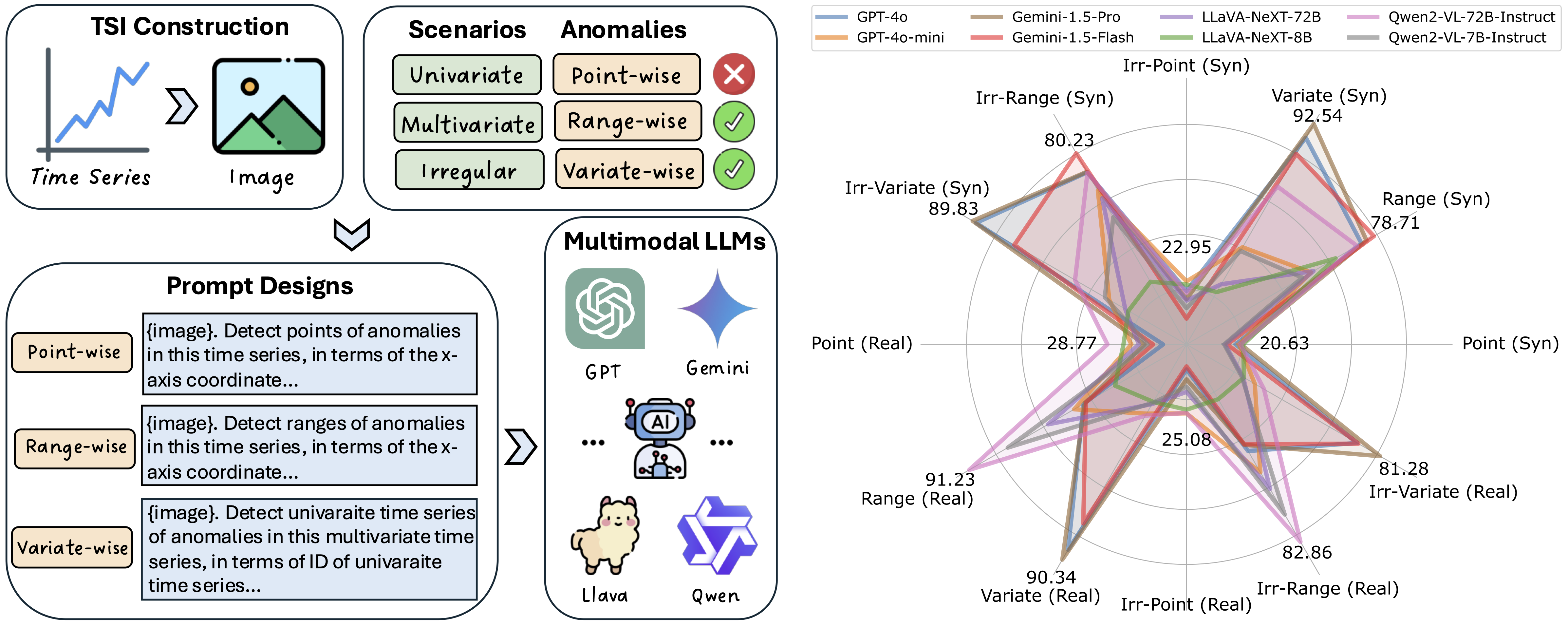
Large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly used in time series analysis. However, the potential of multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), particularly vision-language models, for time series remains largely under-explored. One natural way for humans to detect time series anomalies is through visualization and textual description. Motivated by this, we raise a critical and practical research question: Can multimodal LLMs perform time series anomaly detection?
To answer this, we propose the VisualTimeAnomaly benchmark to evaluate MLLMs in time series anomaly detection (TSAD). Our approach transforms time series numerical data into the image format and feed these images into various MLLMs, including proprietary models (GPT-4o and Gemini-1.5) and open-source models (LLaVA-NeXT and Qwen2-VL), each with one larger and one smaller variant. In total, VisualTimeAnomaly contains 12.4k time series images spanning 3 scenarios and 3 anomaly granularities with 9 anomaly types across 8 MLLMs. Starting with the univariate case (point- and range-wise anomalies), we extend our evaluation to more practical scenarios, including multivariate and irregular time series scenarios, and variate-wise anomalies. Our study reveals several key insights:
1) MLLMs detect range- and variate-wise anomalies more effectively than point-wise anomalies;
2) MLLMs are highly robust to irregular time series, even with 25% of the data missing;
3) open-source MLLMs perform comparably to proprietary models in TSAD. While open-source MLLMs excel on univariate time series, proprietary MLLMs demonstrate superior effectiveness on multivariate time series.
@article{xu2025can,
title={Can Multimodal LLMs Perform Time Series Anomaly Detection?},
author={Xu, Xiongxiao and Wang, Haoran and Liang, Yueqing and Yu, Philip S and Zhao, Yue and Shu, Kai},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.17812},
year={2025}
}
@article{xu2025beyond,
title={Beyond Numbers: A Survey of Time Series Analysis in the Era of Multimodal LLMs},
author={Xu, Xiongxiao and Zhao, Yue and Philip, S Yu and Shu, Kai},
journal={Authorea Preprints},
year={2025},
publisher={Authorea}
}